What is LAN? (Local Area Network)
Published: 24 Nov 2025
Think about all the computers, printers, and phones in your home or office. A Local Area Network (LAN) is what connects them together privately, usually in one building or a small group of buildings nearby. It lets these devices share things like files, printers, and even your internet connection. Unlike the huge internet that spans the whole world, a LAN is just for your local space. Most LANs use wires called Ethernet cables or wireless signals we call Wi-Fi. This technology has been around since the 1970s, starting in offices. Today, whether it’s your home Wi-Fi or your office setup, a LAN is the essential foundation that makes your local devices talk to each other quickly and efficiently. Let’s dive to get the information about Local Area network.
Definition of LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers, devices, and resources within a small geographic area, such as a home, office, or school. It enables devices to communicate with each other and share resources like files, printers, and internet connections. LANs can be wired, using Ethernet cables, or wireless, using Wi-Fi.
History of LAN
The history of Local Area Networks (LANs) dates back to the 1960s when the need for connecting computers in research environments first arose. Early systems like ARPANET, developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, laid the foundation for networking technology. These systems allowed researchers at different locations to share information and access data. In the 1970s, Ethernet was developed by Xerox PARC (Palo Alto Research Center), which became the dominant technology for wired LANs. Ethernet’s ability to transmit data efficiently at high speeds helped the concept of LANs gain momentum in various industries, making them a crucial part of modern communication.
In the 1980s and 1990s, LAN technology evolved rapidly with the introduction of wireless networking. Wi-Fi, or wireless LAN (WLAN), became more accessible, allowing devices to connect without physical cables. This development significantly improved mobility and ease of use, especially in office and home environments. Over the years, the capacity and speed of LANs increased, with advancements in fiber optics and more powerful routers. Today, LANs are ubiquitous, providing essential connectivity for homes, businesses, and educational institutions, allowing for seamless communication and resource sharing.
Working of LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) functions by connecting various devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school, allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other. The key components of a LAN include routers, switches, cables (for wired connections), and network interface cards (NICs) in devices like computers and printers. Routers control the traffic flow between devices and the internet, while switches manage communication between devices within the LAN. For a wired LAN, Ethernet cables physically connect the devices, whereas a wireless LAN uses radio waves (Wi-Fi) for connection.
The working procedure of a LAN begins when devices connect to the network through a router or switch. For wired connections, Ethernet cables link the devices to the switch or router, creating a stable connection. In a wireless LAN, devices connect to the router via Wi-Fi. The router assigns IP addresses to devices on the network, allowing them to communicate. Data is then transmitted over the LAN by routing it through the switch, ensuring that the correct device receives the information.
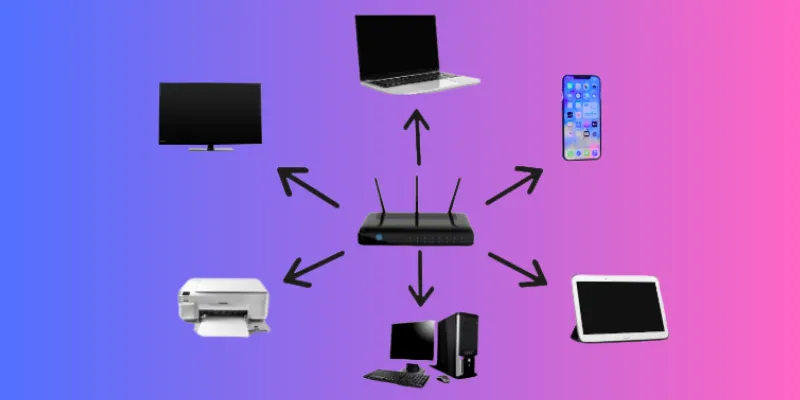
Components of LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) consists of several key components that work together to enable devices to communicate and share resources. The primary components include:
1. Router
The router connects the LAN to external networks, such as the internet, and manages data traffic between devices within the LAN. It assigns unique IP addresses to devices, ensuring proper communication.
2. Switch
A switch connects multiple devices within the LAN, enabling them to communicate directly with each other. It forwards data between devices on the network based on their MAC addresses, ensuring the data reaches the correct device.
3. Ethernet Cables
In a wired LAN, Ethernet cables physically connect devices like computers, printers, and routers to the network. These cables transmit data between devices at high speeds and with low latency.
4. Wireless Access Point (WAP)
For wireless LANs, a wireless access point (WAP) allows devices like laptops and smartphones to connect to the network without the need for cables. The WAP communicates with the router to facilitate wireless communication.
5. Network Interface Card (NIC)
Every device on a LAN needs a Network Interface Card (NIC) to connect to the network. The NIC enables communication between the device and the network, whether through Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
6. Devices
Devices such as computers, printers, smartphones, and servers are the endpoints in a LAN. They use the network to share resources, communicate, and access the internet.
Types of LAN
1. Wired LAN
A Wired LAN is a type of local area network where all the computers and devices are connected using physical cables, such as Ethernet cables. It is commonly used in offices, schools, and homes because it provides a very stable and fast connection. The data travels through the wires, so it is less likely to face interference or signal loss. Wired LANs are also more secure than wireless networks because it is harder for someone to access the network without being physically connected. The setup includes devices like routers, switches, and network interface cards (NICs). Although it requires more work to install due to the need for cabling, it offers high performance and reliability. Wired LANs are preferred in environments where speed and security are very important. However, it can be less flexible because devices cannot easily move around without unplugging and reconnecting cables.
2. Wireless LAN (WLAN)
A Wireless LAN, or WLAN, connects devices without using any cables. Instead, it uses radio waves to transmit data between devices. It is commonly seen in homes, cafes, airports, and schools, where users need mobility and convenience. A wireless LAN uses a device called a wireless router or access point to send signals to laptops, smartphones, or tablets. WLANs are very flexible because users can move around while staying connected. However, they are usually slower than wired LANs and can be affected by walls or other devices. Security is another concern because wireless signals can be picked up by anyone nearby, so strong passwords and encryption are needed. WLAN is great for areas where installing wires would be difficult or expensive. It allows more freedom of movement, which makes it very popular in modern networks.
3. Peer-to-Peer LAN
In a Peer-to-Peer LAN, all the computers in the network are equal and share resources directly with each other. There is no central server managing the network. Each device can act as both a client (requesting data) and a server (providing data). This type of LAN is simple to set up and is often used in small offices or home networks. Since there is no central control, users can easily share files, printers, and other resources. However, it can become hard to manage if the number of devices grows too large. Security and performance may also decrease as more users join. Peer-to-peer networks are cost-effective because they don’t require expensive servers or IT professionals. They are best suited for networks with a small number of users who need to share basic resources. Despite their simplicity, they may not be the best choice for larger or more complex environments.
4. Client-Server LAN
A Client-Server LAN is a network where one or more central servers manage and provide resources to client devices (like computers or printers). The server handles tasks like file storage, security, user access, and printing. This type of LAN is commonly used in businesses, schools, and organizations that require centralized control. Clients can request services from the server, and the server responds with the requested data. It is more secure and organized than a peer-to-peer network. Although it is more expensive to set up due to the cost of servers and maintenance, it offers better performance, reliability, and scalability. This LAN type allows administrators to manage the network efficiently from one place. As more users or devices are added, it can handle the load more effectively than a peer-to-peer LAN. It’s ideal for larger or more complex environments where strong management and control are needed.
5. Token Ring LAN
A Token Ring LAN is a special type of LAN where all the devices are connected in a circular format, forming a logical ring. In this network, a small data packet called a “token” travels around the ring, and only the device that holds the token can send data. This system avoids data collisions and ensures that every device gets a fair chance to transmit. It was developed by IBM and was popular in the past, but it is rarely used today due to the rise of faster Ethernet networks. Token Ring networks can be reliable in preventing data clashes, but they are slower and more expensive to set up compared to modern alternatives. If the token is lost or if one device fails, the entire network can be affected. This network type is now considered outdated but is still a good example of how older technologies managed network traffic.
6. Optical LAN
An Optical LAN uses fiber optic cables to connect devices, which allows it to transmit data at extremely high speeds over long distances. Fiber optics use light signals instead of electrical signals, which means data can move faster and without interference. This type of LAN is used in places that require high performance and reliability, like data centers, hospitals, and large campuses. Optical LANs are more expensive than traditional LANs because fiber cables and related equipment cost more. However, they are more energy-efficient and need less maintenance in the long run. Optical LANs also support more users and devices at once without slowing down. They are known for their excellent quality, durability, and security. Although not commonly used in small networks, they are growing in popularity as the need for faster and more stable internet connections increases.
7. Virtual LAN (VLAN)
A Virtual LAN, or VLAN, is a type of LAN that allows devices on different physical networks to behave as if they are on the same local network. This is done by grouping devices logically instead of physically. For example, in a large company, employees from different departments can be placed into separate VLANs even if they are not in the same building. VLANs are useful for improving network performance, security, and organization. They help reduce unnecessary traffic by isolating devices and can make managing large networks easier. VLANs are usually configured using special network switches and software. One big advantage is that they allow flexibility in designing networks without needing to change the actual wiring. They are commonly used in enterprises, universities, and organizations with complex network needs. VLANs make large networks more manageable, secure, and efficient.
| Benefits of Local area network |
|---|
|
A wired LAN uses Ethernet cables to physically connect devices, providing a stable and faster connection. A wireless LAN uses radio waves (Wi-Fi) to connect devices without cables, offering flexibility but often at a slower speed. Both have their advantages depending on the situation.
Yes, a LAN is ideal for gaming, especially in a local environment. It allows multiple players to connect their devices for multiplayer games without needing the internet. This provides a fast and lag-free gaming experience.
To set up a LAN at home, you’ll need a router, some network cables (for wired LAN), and a few devices like computers or printers. For a wireless LAN, ensure your router has Wi-Fi capabilities, and connect your devices to the network. Follow the router’s instructions to set it up and configure it.
A LAN makes it easier to share files, printers, and internet access between multiple devices. It also allows faster communication within the network. Additionally, it can save money by enabling shared resources instead of buying separate devices.
A LAN can be secure if you take proper precautions, like using strong passwords and enabling firewalls. For wireless LANs, encryption methods like WPA2 can protect your data from unauthorized access. Regular updates and secure connections are key to keeping a LAN safe.
A typical wired LAN can cover distances of up to 100 meters per Ethernet cable, while wireless LANs (Wi-Fi) usually cover areas within a home or office, ranging from 30 to 100 meters. The range depends on the router and the environment.
Conclusion
So guys, in this article, we’ve covered Local Area Network (LAN) in detail. From understanding how LANs work to exploring their components, benefits, and security considerations, you should now have a solid grasp of what a LAN can do for you. If you’re setting up a network for your home or office, I highly recommend considering the right LAN setup based on your needs—whether it’s wired or wireless. Take the time to evaluate your requirements and set up your own efficient LAN today. Don’t hesitate to dive deeper and start building your network!

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks