Barcode Scanner and its types Simplify Your World
Published: 6 Jun 2025
Did you know that barcode readers process billions of scans worldwide every day? From grocery stores to airports, these handy devices help businesses track products, manage inventory, and speed up transactions. But did you know there are different types of barcode readers, each designed for specific needs? Let’s explore the Barcode scanner and its types in detail.
1. Introduction
A barcode scanner is a device used to read and decode the information contained in barcodes. Barcodes are patterns of lines or squares that hold product details or inventory data. There are several types of barcode scanners, including pen-type, laser, CCD, camera-based, omni-directional, and 2D scanners, each designed for specific uses based on the complexity of the barcode and scanning environment.
2. How it Works?
A barcode Scanner works by scanning a barcode and converting it into readable data. Here’s how the process works:
- Light Source: The scanner uses either a laser or LED light to shine on the barcode.
- Sensor: The sensor detects the reflected light from the barcode.
- Decoder: The decoded information from the barcode is then sent to the decoder, which translates it into usable data.
- Transmitter: The decoded data is transmitted to a connected system (like a computer)
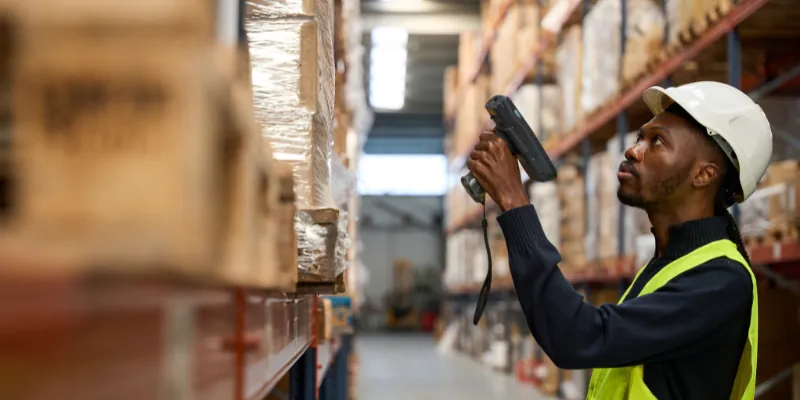

3. Different types of scanners
- Pen-Type Scanners: The user manually moves the pen across the barcode.
- Laser Scanners: Use laser beams to scan barcodes and reflect light.
- CCD Scanners: Capture light from multiple points to read the barcode.
- Camera-Based Scanners: Take a digital image of the barcode and decode it.
- Omni-Directional Scanners: Can scan barcodes from any angle.
- 2D Scanners: Read both 1D and 2D barcodes, such as QR codes.
1. Pen-Type Barcode Scanner
A pen-type barcode Scanner uses a light sensor that moves across the barcode. When the sensor moves over the barcode, it shines a light (often from a diode) on the lines of the barcode. The sensor detects the reflection from the barcode’s black and white bars. As the sensor moves, it collects the reflected light, which is then decoded into data by the scanner. The data is sent to a connected system, such as a computer or register, for processing.
Uses
- Small retail shops
- Libraries for checking out books
- Inventory management in small stores
- Personal use for organizing home inventory
- Scanning barcode labels on packages
- Price verification in stores
- Used in light-volume warehouses
| Advantages of Pen-type Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Pen-type Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
2. Laser Barcode Scanner
Laser barcode scanners use a laser beam to scan barcodes. The scanner directs the laser beam onto the barcode, and the light reflects back into a sensor. The reflected light is analyzed to decode the pattern of bars into digital data. Laser scanners usually emit a red light laser, and the scanner processes the reflection in real time. This type of scanner works well with both printed and digital barcodes.
Uses
- Supermarket checkout counters
- Large retail stores for product sales
- Warehouses for inventory management
- Pharmaceutical industry for prescription scanning
- Libraries for book tracking
- Hospitals for patient identification
- Ticketing systems for events and transportation
| Advantages of laser Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of laser Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
3. CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) Barcode Scanner
CCD barcode scanners use an array of light sensors arranged in a grid pattern to capture the reflected light from a barcode. The scanner’s light sensors work by capturing light from different points on the barcode, converting the light patterns into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to the decoder, which processes them into digital data that can be read by the system. CCD scanners generally do not require moving parts, making them highly durable.
Uses
- Small to medium-sized retail businesses
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems
- Libraries and book rental services
- Simple inventory management for small businesses
- Scanning product labels in logistics
- Ticket scanning for public transport
- Mobile device scanning for small businesses
| Advantages of CCD |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of CCD |
|---|
|
4. Camera-Based (Imager) Barcode Scanner
Camera-based barcode scanners use a camera to take a digital image of a barcode. The camera captures the barcode’s two-dimensional image, which is then processed by the scanner’s software. The scanner decodes both 1D and 2D barcodes, including QR codes. Since the scanner works by capturing an image, it is capable of scanning barcodes from different angles and can read barcodes displayed on screens (e.g., smartphone screens).
Uses
- Scanning QR codes for mobile payments
- Airline boarding passes
- Event ticketing and mobile check-ins
- Retail systems for reading product codes
- Logistics and package tracking
- Warehouse management for complex inventories
- Healthcare for scanning medication or patient labels
| Advantages of Camera-Based Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Camera-Based Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
5. Omni-Directional Barcode Scanner
Omni-directional scanners use multiple laser beams arranged in a pattern, allowing them to scan barcodes from any angle. These scanners generate a 360-degree pattern of laser beams, which enables them to read barcodes without having to align them precisely. The scanner then analyzes the reflections from the barcode, decodes the data, and transmits it to the connected system. This feature makes them ideal for high-speed scanning environments.
Uses
- High-traffic retail environments (e.g., supermarkets, department stores)
- Self-checkout systems
- Warehouse and logistics operations
- POS systems in busy environments
- Event check-in systems
- Airline check-in counters
- Large-scale product scanning and inventory systems
| Advantages of Omni-Directional Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Omni-Directional Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
6. 2D Barcode Scanner
2D barcode scanners are designed to read both 1D and 2D barcodes. These scanners use imaging technology to capture a 2D barcode’s full data pattern. The captured image is processed by the scanner’s software to decode the barcode, which can contain more information than a traditional 1D barcode. 2D scanners can read barcodes in different orientations, which increases their versatility compared to traditional scanners.
Uses
- Scanning QR codes for mobile payment systems
- Ticket scanning at events, cinemas, and public transport
- Product labeling and inventory tracking
- Loyalty programs and customer rewards (e.g., digital coupons)
- Packaging in industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics
- Scanning barcodes from mobile devices (e.g., smartphone apps)
- Healthcare systems for patient and medication tracking
| Advantages of 2D Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of 2D Barcode Scanner |
|---|
|
4. How to Choose the Right Barcode Scanner
Choosing the right barcode scanner depends on several factors, including the type of barcodes you need to scan, your budget, and the environment in which the scanner will be used. Here are some key considerations:
Barcode Type: If you only need to scan traditional 1D barcodes (like those found on products), a basic laser or CCD scanner may be enough. However, if you need to scan 2D barcodes (such as QR codes), opt for a 2D imager or camera-based scanner.
Scanning Environment: For a high-volume retail setting with fast-paced checkout lines, an omni-directional scanner can be ideal as it can scan barcodes from any angle quickly. For warehouse environments, a long-range scanner may be needed for scanning barcodes from a distance.
Durability: If the scanner will be used in tough environments (like warehouses or construction sites), you’ll need a more rugged model that can withstand drops, dust, and moisture. Look for scanners with an IP rating for water and dust resistance.
Connection Type: Decide whether you need a wired or wireless scanner. Wired scanners are more reliable but can be limited by cable length, while wireless scanners offer more mobility but require charging and range management.
Budget: Basic pen-type and CCD scanners are more affordable but limited in functionality. Laser and 2D scanners may cost more but provide better flexibility and features for diverse business needs.
A barcode reader is a device that scans and decodes information stored in barcodes. Barcodes are printed patterns of lines or squares that contain product or inventory information. The reader translates the barcode into data, making it easy to process or track items.
Barcode readers use light or a camera to capture the pattern of a barcode. This information is then converted into digital data and sent to a computer or register. The reader interprets the barcode’s unique code to identify the product or item.
1D barcodes are the traditional linear barcodes you often see on products. 2D barcodes, like QR codes, store more information and appear as a grid of dots or squares. 2D scanners can read both types, but 1D scanners can only read linear barcodes.
Yes, smartphones can scan barcodes using built-in cameras and apps. Many apps are designed to read both 1D and 2D barcodes. However, they are slower and less durable than specialized barcode readers.
For a small business, a CCD or laser barcode scanner should work well. They’re affordable, easy to use, and accurate for everyday tasks. Consider wireless options if you need mobility or to reduce clutter.
Yes, many barcode readers come in wireless models. These models connect to your computer or system via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing for more flexibility. However, wired models are still common and often more affordable.
When choosing a barcode reader, think about the types of barcodes you’ll be scanning and the environment. For high-volume scanning, an omnidirectional scanner might be best. If you need to scan QR codes or mobile tickets, look for a 2D scanner.
Most modern barcode readers can handle slightly damaged or dirty barcodes. However, if a barcode is too damaged or smudged, it might not scan correctly. Regularly check barcodes to ensure they are clear and clean.
Barcode readers are generally very accurate when used correctly. Errors can occur if the barcode is damaged, dirty, or poorly printed. Using the right type of scanner for your needs can help reduce mistakes.
Barcode readers don’t require much maintenance, but keeping the lens clean is important for accurate scanning. Occasionally check for software or firmware updates if your reader connects to a computer. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for care.
Conclusion
So guys, in this article, we’ve covered Barcode Reader and Its Types in detail. Whether you’re a small business owner or simply someone curious about how barcode scanning works, I hope this guide has helped. I personally suggest looking at factors like durability and compatibility with your system before making a purchase. Don’t rush the decision, find the right barcode reader that will make your processes smoother and faster. Ready to dive in? Start exploring your options now!

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks